Highlights
- Cybercrime continues to be a major financial burden worldwide, with losses projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025
- The cyber insurance market in the U. S. is expected to grow to $20 billion by 2025, as businesses seek protection against cyber risks.
- Financial institutions in the U.S. spent over $150 billion on cybersecurity measures in 2024 to combat cyber threats.
- Companies in the U.S. lose between $500 billion and $1 trillion annually as a result of business downtime and lost productivity due to malware incidents.
Introduction
Cybercrime refers to all criminal activities carried out using computers, networks, or digital devices, often targeting individuals, businesses, or governments. These crimes can involve hacking, fraud, identity theft, cyberstalking and online piracy. They can also involve any and all sectors.
Cybercrime affects national security, critical infrastructure, and public trust. Businesses and companies face operational disruptions, financial losses, reputational damage and regulatory fines due to cyberattacks while individuals suffer from identity theft, fraud, and personal financial losses.
The widespread adoption of the internet has contributed to the significant rise in cybercrimes. Governments and organizations worldwide have had to implement cybersecurity laws and regulations to combat digital threats.
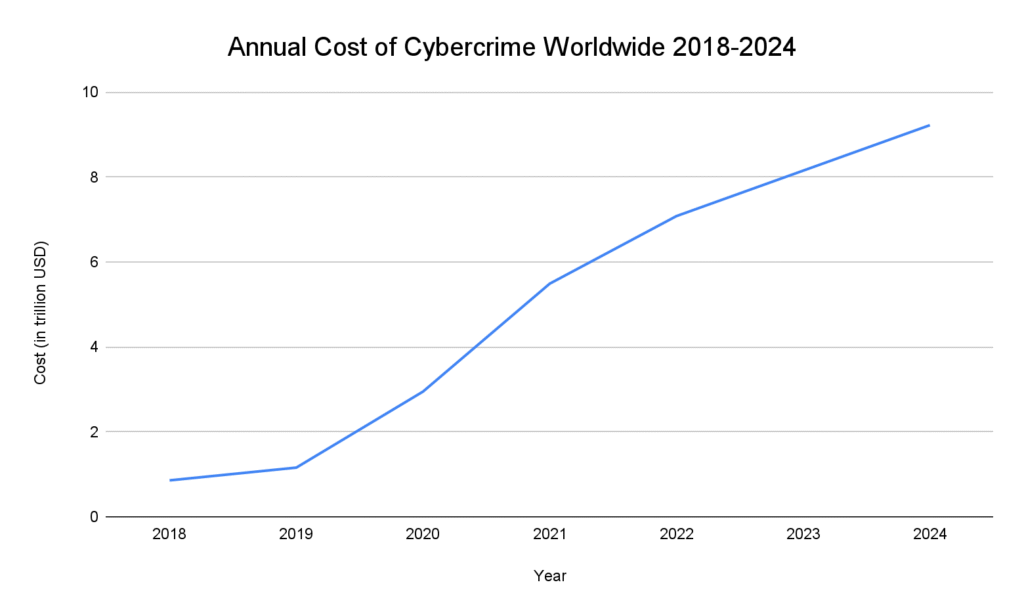
Cost of Cybercrime by Year
Cost of Cybercrime in 2020
- In 2020 the total global cybercrime losses were estimated at $945 billion, with an additional $145 billion spent on cybersecurity measures.
- The McAfee report estimated cybercrime losses at over $1 trillion globally, a 50% increase from 2018.
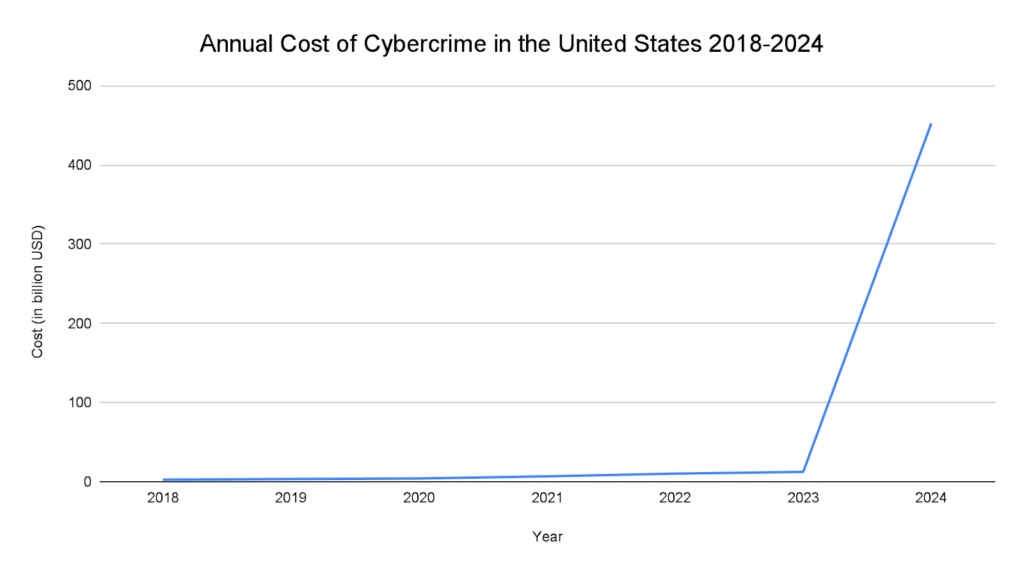
- Cybercrime had a major financial impact in the U. S. in 2020, with losses exceeding $4.2 billion, according to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3).
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams were the most costly, accounting for $1.8 billion in losses.
- Phishing attacks doubled in 2020, with 241,342 victims, compared to 114,702 victims in 2019.
- One of the most significant cyberattacks in 2020 was the SolarWinds cyberattack in the U.S., which affected government agencies, private companies, and critical infrastructure.
- Hackers infiltrated SolarWinds’ Orion software, compromising U.S. federal agencies, including the Department of Homeland Security and Treasury Department.
- The attack was attributed to nation-state actors, causing widespread security concerns and financial damages.
Cost of Cybercrime in 2021
- Financial losses from cybercrime reached $6 trillion in 2021, marking a significant increase from previous years.
- The U.S. alone reported cybercrime losses of $6.9 billion, with thousands of businesses affected.
- Investment fraud caused the highest financial losses, totaling $1.45 billion.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams ranked second, with losses reaching $2.4 billion.
- One of the most significant cyberattacks in 2021 was the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack, which disrupted fuel supplies across the United States.
- The attack was carried out by the DarkSide ransomware group, forcing Colonial Pipeline to shut down operations.
- The company paid a $4.4 million ransom to regain control of its systems, although U.S. authorities later recovered a portion of the funds.
Cost of Cybercrime in 2022
- The global cost of cybercrime was estimated at $8.4 trillion, making it one of the most expensive criminal activities worldwide.
- Losses from cybercrime in the U.S. exceeded $10.3 billion. This marked a 49% increase compared to 2021, despite a 5% decrease in the number of complaints.
- Investment fraud was the leading cause of financial loss, accounting for $3.3 billion, followed by business email compromise (BEC) scams, which resulted in $2.74 billion in losses.
- One of the most significant cybercrime events in 2022 was the Twitter data breach in November, where 5.4 million user records were leaked on a hacker forum due to an API vulnerability.
- While most of the exposed data was public, some records contained private information like phone numbers and email addresses
- The Uber security breach in 2022 was a major cybersecurity incident in the U.S.
- A hacker affiliated with the Lapsus$ group infiltrated Uber’s internal systems, including its Slack server, Amazon Web Services panel, and Google Workspace email admin dashboard.
- The attacker gained access using credentials from a third-party vendor, likely purchased from the dark web.
Cost of Cybercrime in 2023
- Globally, cybercrime losses reached $8 trillion in 2023, occurring at a rate of $667 billion per month.
- The U. S. alone reported cybercrime losses of $12.5 billion, marking a significant increase from previous years.
- In 2023, there was a rise in investment fraud and business email compromise (BEC) scams, which accounted for 60% of all reported financial losses.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams led to $2.9 billion in losses in the U. S..
- A major incident was the MOVEit data theft, where cybercriminals exploited a zero-day vulnerability in the popular file transfer software MOVEit, affecting thousands of organizations across various sectors, including media and healthcare
- One of the most significant cybercrime events in the U.S. in 2023 was the theft of U.S. State Department records.
- Hackers breached Microsoft Exchange and stole tens of thousands of emails, including at least 60,000 emails from the Outlook accounts of the U.S. State Department personnel.
Cost of Cybercrime in 2024
- The global cost of cybercrime in 2024 was estimated to be between $9.22 trillion and $9.5 trillion
- In the U. S. cybercrime costs reached approximately $452.3 billion and some estimates also suggest cyber theft alone cost the U.S. economy over $350 billion
- In 2024, the world witnessed the rise of cybercrime-as-a-service, where experienced cybercriminals sold hacking tools to others, resulting in several high-profile attacks that disrupted industries worldwide.
- One of the most significant global cybercrime events was the Change Healthcare ransomware attack, which crippled healthcare services in the U.S. for weeks
- The BlackCat (ALPHV) ransomware group infiltrated Change Healthcare’s systems, halting electronic payments and medical claims processing, affecting hospitals and pharmacies.
- Another major global cyberattack was the Snowflake data breach, where cybercriminals exploited security gaps in the cloud storage provider, compromising sensitive data from companies like AT&T, Ticketmaster, and Santander Bank.
- In the U.S., the Salt Typhoon cyberattack targeted nine major telecommunications companies, including AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile.
- Hackers exploited unpatched vulnerabilities to steal sensitive communications data and geolocation information.
- Additionally, the U.S. Treasury Department suffered a cyberattack in December, where hackers infiltrated systems using vulnerabilities in BeyondTrust’s remote support software
Cost of Cybercrime in 2025
- Cybercrime continues to be a major financial burden worldwide, with losses projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) reports that if cybercrime were an economy then it would rank as the third-biggest economy globally, trailing only the U. S. and China.
- Ransom payments have increased by 500%, reaching an average of $2 million.
- Cybercrime continues to be a major financial burden in the U. S., with losses projected to reach $12.5 billion in 2025.
- 33% of device vulnerabilities in 2025 originated from IoT and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) systems.
- About 40% of 2025’s cyber incidents involved AI-driven tactics, including adaptive malware.
- The cyber insurance market is expected to grow to $20 billion by 2025, as businesses seek protection against cyber risks.
- Cyber insurance premiums in the U.S. are projected to grow from $14 billion in 2023 to $29 billion by 2027, as businesses seek protection against cyber risks.
Top 10 Countries With Citizens Submitting Cybercrime Complaints to The Internet Crime Complaint Center in 2024
| Country | Number of Complaints |
|---|---|
| United Kingdom | 102,692 |
| Canada | 6,951 |
| India | 4,189 |
| France | 2,223 |
| Philippines | 1,790 |
| Australia | 1,533 |
| Germany | 1,524 |
| Japan | 1,492 |
| Brazil | 1,472 |
| Honduras | 1,352 |
Cost of Cybercrime by Sector
Cost of Cybercrime in Banking.
- Since 2020, direct cybercrime losses in the financial sector have amounted to $2.5 billion.
- Nearly one-fifth of reported cyber incidents have targeted financial institutions, making them a prime target
- Ransomware attacks on financial services in th U. S. have increased from 55% in 2022 to 64% in 2023, nearly double the rate from 2021
- Ransomware attacks alone cost U.S. financial institutions over $5 million per incident, excluding ransom payments
- The average annual loss (AAL) rate from cyber incidents varies by bank size, with smaller banks facing higher proportional losses
- Over the past two years, U.S. banks have seen a 66.8% increase in social engineering attacks, leading to millions in losses per incident
Cost of Cybercrime in Utilities
- Attacks on energy grids, water systems, and telecommunications have disrupted essential services, making cybersecurity a top priority for the sector.
- 87% of utility companies have experienced at least one data breach in the past three years.
- Cyberattacks on operational technology (OT) systems in utilities are ranked among the top five most significant risks by the World Economic Forum
- A cyberattack on a U.S.-based utility resulted in the loss of 90% of its internal systems and wiped out 25 years of historical data.
- In the last three years, U.S. businesses specializing in manufacturing and utilities have suffered 562 data breaches, compromising nearly 91 million records.
- The estimated financial impact of these breaches exceeds $14.7 billion, with 2022 alone accounting for $6 billion in losses.
Cost of Cybercrime in Software
- Cybercrime has inflicted significant financial losses on the software sector in recent years, with attacks targeting intellectual property, cloud infrastructure, and customer data
- Ransomware attacks on software companies surged by 30% between 2023 and 2024, leading to billions in losses.
- Ransomware attacks on software companies have surged, with damages expected to reach $265 billion annually by 2031
- Software vulnerability detections increased by over 25% in 2022, highlighting the growing risks for tech firms
- Software supply chain attacks have surged, with over 60% of tech firms reporting breaches linked to third-party vendors.
- Cyber insurance premiums for software firms increased by 40% in 2024, reflecting the growing risk of cyberattacks.
Cost of Cybercrime in Automotive
- Cybercrime has inflicted tens of billions of dollars in losses on the automotive sector from 2022 to 2024, with attacks targeting ransomware, data breaches, and operational disruptions.
- From 2021 to mid-2023, ransomware damage costs in the automotive industry surged by over 180%, rising from $74.7 million to $209.6 million.
- System downtime costs caused by cyberattacks reached $1.99 billion in the first half of 2023
- Massive-scale cyber incidents affecting millions of vehicles in the U. S. more than tripled between 2023 and 2024, accounting for 60% of all incidents
- Automotive vulnerabilities in the U. S. reached an all-time high in 2024, with 77% of security flaws found in onboard or in-vehicle systems
- Electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure has become a new target, with unsecure payment protocols and outdated communication standards posing risks to both vehicles and power grids.
Cost of Cybercrime in Insurance
- The global cyber insurance market is expected to grow to $16.3 billion in 2025, reflecting the increasing demand for cybersecurity coverage.
- The largest cyber event to date, NotPetya (2017), resulted in more than $10 billion in losses, with up to $3 billion covered by the insurance sector
- Cyber insurance claims exceeding €1 million rose 14% in frequency and 17% in severity in 202
- Ransomware attacks on insurance companies surged by 30% between 2023 and 2024, leading to billions in losses.
- The U.S. insurance sector reported cybercrime losses exceeding $10 billion in 2024, with attacks on policyholder databases and claims processing systems being the most severe.
- Regulatory compliance costs for insurance firms have risen due to stricter cybersecurity laws and data protection requirements.
Cost of Cybercrime in Energy
- Nation-state cyber espionage has intensified, with adversaries targeting nuclear facilities, oil and gas infrastructure, and renewable energy grids
- For example, the 2015 cyberattack on Ukraine’s power grid resulted in temporary price hikes as the country had to rely on more expensive sources of electricity.
- In 2022, the energy sector was identified as the UK’s top target for cyber-attacks, accounting for 24% of all cyber-attacks in the country
- In 2023, 90% of the world’s largest energy companies suffered cybersecurity breaches, with critical infrastructure becoming a primary target for cybercriminal
- The U.S. energy sector has faced an unprecedented level of cyber threats, with foreign adversaries increasingly testing security measures
- Between November 2023 and April 2024, 29 cyberattacks specifically targeting the industrial control systems of U. S/ energy infrastructures were reported
Cost of Cybercrime in Health
- The healthcare industry has consistently reported the highest cyberattack costs of any sector.
- In 2023, the average cost of a healthcare data breach was $10.93 million per incident, nearly double that of the financial sector.
- The WannaCry ransomware attack cost the U.K.’s National Health Service (NHS) more than $100 million
- The average cost of a healthcare data breach in the U.S. was $9.77 million in 2025.
- Privacy-related lawsuits have surged, with over 1,300 data breach-related class action lawsuits filed in the U.S. in 2023.
- The largest healthcare breach in U.S. history compromised 100 million patient records.
Cost of Cybercrime by Types of Crime
Cost of Hacking
- Hacking is a type of cybercrime that involves unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, or devices to steal data, disrupt operations, or cause damage.
- While some hacking is ethical (such as penetration testing by cybersecurity professionals), cybercriminals use hacking techniques for malicious purposes and cybercriminal hacking is a major global threat.
- Hacking has devastating consequences, affecting individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. It leads to financial losses, data breaches, identity theft, and operational disruptions.
- In 2024, data breaches exposed 422.61 million records, impacting millions worldwide and the average cost of a data breach globally was $4.88 million.
- Phishing attacks skyrocketed by 4,151% since the public release of AI-powered tools.
- The average cost of a data breach in the U.S. was $4.88 million in 2024.
Cost of Fraud
- Fraud as a cybercrime involves deception to gain financial or personal benefits through digital means. Cybercriminals use various tactics to manipulate victims into providing sensitive information or making fraudulent transactions.
- Global financial fraud losses reached $485 billion in recent years.
- Scammers stole over $1 trillion globally in just 12 months, according to the 2024 Global State of Scams report.
- Fraud now accounts for 40% of all crime in the UK, highlighting its widespread impact.
- The U. S. government lost an estimated $233 billion to $521 billion annually to fraud between 2018 and 2022.
- Online fraud cases in the U.S. surged, with cybercrime incidents rising from 467,000 in 2019 to over 880,000 in 2023.
Cost of Identity Theft
- Identity theft is a type of cybercrime where criminals steal personal information to commit fraud or other illegal activities.
- The market for identity theft protection services is projected to reach $28 billion by 2029.
- In 2024, the total estimated losses from identity theft in the U.S. were $10.2 billion and the median financial loss for identity theft victims was $500.
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) received 5.7 million fraud and identity theft reports, with 1.4 million cases specifically related to identity theft.
- Identity theft cases are occurring at an alarming rate, with a new victim every 22 seconds in the U.S..
- Criminals are increasingly using synthetic identities—combining real and fake information—to commit fraud and it accounted for 80% of all credit card fraud losses in 2022.
Cost of Malware
- Malware, short for malicious software, is a type of cybercrime where harmful programs are designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems.
- Cybercriminals use malware to spy on users, steal sensitive data, extort money or sabotage networks.
- The global cost of ransomware alone is projected to exceed $275 billion by 2031, with a new attack occurring every 2 seconds.
- In 2025, ransomware damages are expected to reach $57 billion annually, breaking down to $4.8 billion per month.
- The U.S. cybersecurity market has seen a rise in malware-related damages, with businesses and government agencies investing heavily in cybersecurity.
- Companies lose between $500 billion and $1 trillion annually as a result of business downtime and lost productivity due to malware incidents.
Types of Cybercrime Complaints and Losses Reported to The Internet Crime Complaint Center in 2024
| Crime Type | Complaints | Losses |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing/Spoofing | 193,407 | $70,013,036 |
| Personal Data Breach | 64,882 | $1,453,296,303 |
| Investment | 47,919 | $6,570,639,864 |
| Business Email Compromise | 21,442 | $2,770,151,146 |
| Identity Theft | 21,403 | $174,354,745 |
| Credit Card/Check Fraud | 12,876 | $199,889,841 |
| Data Breach | 3,204 | $364,855,818 |
| Ransomware | 3,156 | $12,473,156 |
| Malware | 441 | $1,365,945 |
Conclusion
Cybercrime remains a growing threat, requiring strong cybersecurity measures, international cooperation, and continuous innovation to mitigate risks.
AI-driven cyberattacks are expected to increase, making cybercrime more sophisticated.
Government agencies and private companies are investing in AI-driven security solutions to detect and prevent cyberattacks.
References
- https://www.britannica.com/topic/cybercrime
- https://www.mdpi.com/2673-6756/2/2/28
- https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5a82d166e5274a2e8ab59814/understanding-costs-of-cyber-crime-horr96.pdf
- https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/understanding-the-costs-of-cyber-crime
- https://www.statista.com/forecasts/1399040/us-cybercrime-cost-annual
- https://www.tripwire.com/state-of-security/cost-cybercrime-us-facts-and-figures
- https://soax.com/research/cost-of-cybercrime
- https://cybersecurityventures.com/cybercrime-damage-costs-10-trillion-by-2025/
- https://www.techradar.com/news/cybercrime-cost-the-world-over-dollar1-trillion-in-2020
- https://www.comsuregroup.com/news/1-trillion-mcafee-report-on-the-hidden-costs-of-cybercrime/
- https://www.vadesecure.com/en/blog/cybercrime-statistics-top-threats-and-costliest-scams-of-2020
- https://www.comsuregroup.com/news/1-trillion-mcafee-report-on-the-hidden-costs-of-cybercrime/
- https://cybersecurityforme.com/cybercrime-statistics/
- https://www.getastra.com/blog/security-audit/cyber-crime-statistics/
- https://vpnalert.com/resources/cyber-crime-statistics/
- https://www.ic3.gov/AnnualReport/Reports/2021_IC3Report.pdf
- https://www.cnet.com/tech/computing/internet-crime-cost-people-more-than-6-9b-in-2021-fbi-says/
- https://www.rutherfordsearch.com/blog/2022/04/cybercrime-costs-to-reach-heights-of-1-pounds-trillion-in-2022
- https://aag-it.com/the-latest-cyber-crime-statistics/
- https://www.techmonitor.ai/partner-content/state-of-cybercrime-2022
- https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/cyber-security-breaches-survey-2022/cyber-security-breaches-survey-2022?pStoreID=fedex%27A
- https://cybersecurityventures.com/cybercrime-to-cost-the-world-8-trillion-annually-in-2023/
- https://www.statista.com/chart/32341/worldwide-reported-losses-connected-to-cybercrime/
- https://cybersecurityventures.com/cybersecurity-almanac-2023/
- https://www.weforum.org/stories/2024/01/cybersecurity-cybercrime-system-safety/
- https://www.statista.com/chart/28878/expected-cost-of-cybercrime-until-2027/
- https://www.verimatrix.com/cybersecurity/knowledge-base/cybercrime-statistics-key-stats-and-insights/
- https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Cybercrime_Atlas_2024.pdf
- https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/cyber-security-breaches-survey-2025/cyber-security-breaches-survey-2025
- https://cybersecurityventures.com/cybersecurity-almanac-2024/
- https://www.brightdefense.com/resources/cybercrime-statistics/
- https://www.cyberdefensemagazine.com/the-true-cost-of-cybercrime-why-global-damages-could-reach-1-2-1-5-trillion-by-end-of-year-2025/
- https://www.spyhunter.com/shm/cyber-crime-statistics/
- https://www.statista.com/forecasts/1280009/cost-cybercrime-worldwide
- https://www.cybersecurityintelligence.com/blog/cyber-crime-cost-the-us-16-billion-in-2024-8405.html
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1464416/global-damage-costs-of-cyberattacks-automotive/
- https://www.munichre.com/en/insights/cyber/cyber-insurance-risks-and-trends-2025.html
- https://www.bdemerson.com/article/complete-cybercrime-statistics
- https://www.crowe.com/global/news/fraud-costs-the-global-economy-over-us$5-trillion
- https://www.fisglobal.com/about-us/media-room/press-release/2025/new-research-by-fis-and-oxford-economics
- https://www.consumeraffairs.com/finance/identity-theft-statistics.html
- https://identitytheft.org/statistics/
- https://scoop.market.us/identity-theft-statistics/
- https://cybersecurityventures.com/global-ransomware-damage-costs-predicted-to-reach-250-billion-usd-by-2031/
- https://www.forbes.com/advisor/education/it-and-tech/cybersecurity-statistics/
- https://www.hipaajournal.com/fbi-losses-to-cybercrime-increased-by-49-in-2022-to-10-3-billion/
- https://www.fbi.gov/contact-us/field-offices/springfield/news/internet-crime-complaint-center-releases-2022-statistics
- https://heimdalsecurity.com/blog/top-cyberattacks-of-2022/
- https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news-features/top-cyber-attacks-2023/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/malware-and-its-types/
- https://csu.org.uk/types-of-cyber-attack/malware-attacks-definition-and-best-practices/
- https://thehackernews.com/2025/05/us-dismantles-danabot-malware-network.html
- https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/lumma-infostealer-malware-operation-disrupted-2-300-domains-seized/
- https://cybersecuritynews.com/cybercrime-2025/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/cyber-crime-identity-theft/
- https://www.kaspersky.co.uk/resource-center/threats/what-is-cybercrime
- https://www.eccouncil.org/cybersecurity-exchange/computer-forensics/cybercrime-types-prevention-digital-forensics/
- https://health-isac.org/wp-content/uploads/Health-ISAC_2025-Annual-Threat-Report.pdf
